Snow zones and wind zones are specified on maps provided in the national annexes to the Eurocode 1. Seism zones are specified on maps provided in the national annexes to the Eurocode 8 or in national legal texts.
What is a snow zone ?
Each country has set characteristic snow loads on the ground for each portion of its territory. The division is usually specified in the national annex of Eurocode 1 part 1-3.
What is a wind zone ?
Each country has set fundamental value of the basic wind velocity for each portion of its territory. The reference velocity corresponds to the average wind velocity over 10 minutes, measured at 10m above ground level on an ‘open country’ site with a return period of 50 years. The division is usually specified in the national annex of Eurocode 1 part 1-4.
What is a seismic zone ?
Each country has set reference peak ground acceleration on type A ground for each portion of its territory. The type A ground has a stratigraphic profile like rock or other rock-like geological formation, including at most 5m of weaker material at the surface. The division is usually specified in the national annex of Eurocode 8 part 1-1.
How to calculate snow on your building site ?
First, you need to calculate the value of snow on the ground at the relevant site :
- depending on the snow zone in which the building is located, according to the map taken from the national annex to the Eurocode 1 part 1-3.
- taking into account the effect of the elevation.
Then, you can take into account the annual probability of exceedence by calculating the ground snow load with a return period equivalent to the design working life of your building.
Why calculate peak velocity pressure by wind direction ?
The wind direction is to be considered for several reasons :
- First, the high velocities of wind are observed more frequently in certain direction sectors; the directional factor accounts for this by authorizing a reduction when the wind comes from a direction where the probability of occurrence of strong winds is less.
- On the other hand, the orography and the roughness of the terrain generally vary with the direction of the wind.
- Finally, the pressure or force coefficients depend on the direction of the wind relative to the construction.
How to calculate peak velocity pressure by wind direction ?
For the calculation of wind actions, only a few wind directions are considered; for example the normal directions to the facades in the case of buildings. To accurately determine the peak velocity pressure, you will have to take into account many parameters such as :
- the wind zone according to the map taken from the national annex to the Eurocode 1 part 1-4.
- the directional factor cdir
- the annual probability of exceedence by calculating the basic wind velocity vb with a return period equivalent to the design working life of your building.
- the roughness factor Cr(z) , to take into account the effect of the environment (vegetation / urbanization).
- the orography factor co(z) , to take in account the effect of terrain relief.
Then you can calculate the wind peak velocity pressure:
\[\displaystyle q_{p(z)} = \left[ 1 + 7 \cdot I_{v(z)}\right] \cdot \frac{1}{2} \cdot \rho \cdot v_{m(z)}^{2} = c_{e(z)} \cdot q_{b}\]- qp is the pressure in newtons per square meter (N/m²)
- Iv(z) is the turbulence intensity, at height z, defined as the standard deviation of the turbulence divided by the mean wind velocity.
- ρ is the air density in kilogram per cubic meter (kg/m3)
- ce is the exposure factor, with the basic velocity pressure qb
How to calculate wind velocity from pressure ?
\[\displaystyle v = 3.6 \cdot \sqrt \frac{q}{0.5 \cdot \rho} \]- v is the velocity in kilometers per hour (km/h).
- q is the pressure in newtons per square meter (N/m²).
- ρ is the air density in kilogram per cubic meter (kg/m3)
Do I need for seismic analysis ?
- In cases of very low seismicity, the provisions of Eurocode 8 need not be observed.
- It is recommended to consider as very low seismicity cases either those in which the design ground acceleration on type A ground, ag = γI . agr , is not greater than 0.39 m/s², or those where the product agS is not greater than 0.49 m/s².
- The seismic zones, the agr values and the chosen method may be found in national Annexes or in the law specific to each country. §3.2.1(5)
- (Description of type A ground: Rock or other rock-like geological formation, including at most 5m of weaker Inaterial at the surface)
Example of a result given by Eurocodes Zoning software
B1 – Localization
- Coordinates in World Geodetic System 1984 (WGS84) 6.9511°, 43.4979°
- Coordinates in French Geodetic System 1993 (Lambert 93) 1019565m, 6274536m
Address 06590 Théoule-sur-Mer, Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur
B2 – Elevations
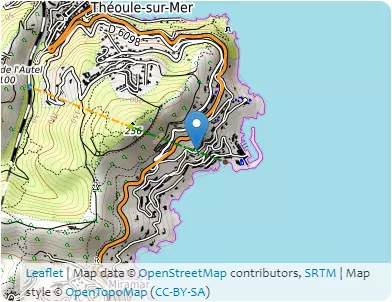
| Coordinates | 6.9536° 43.4972° | 6.9455° 43.4994° | 6.9455° 43.4994° | 6.9368° 43.5019° |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elevations | 9m | 244m | 244m | 54m |
| Obstacle effective height H | 235m | 190m | ||
| Slope actual length Lu / Ld | 698.4m | 754.4m | ||
| Slope angle Φ | 33.7% | 25.2% | ||
| Horizontal distance site/top x | 483.1m | |||
| Elevation at the place of construction | 58m | |||
B3 – Building
- Type of building : common structure
- Design working life category : 50 years
- Max height : 8.0m
- Orientation from North : 15°
B4 – Terrain categories

| Sectors | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Categories | IIIb | 0 | 0 | IIIb |
C1 – Snow
NF EN 1991-1-3/NA (may 2007) + A1 (july 2011)
- Zone : A2(sk,0 = 0.45 kN/m²)
- Criteria for zoning : MANDELIEU-LA-NAPOULE, ALPES-MARITIMES (06)
- Characteristic value of snow on the ground at the relevant site : sk,58 = 0.45 kN/m²
- Ground snow load with a return period of 50 years : s50 ans = 0.45 kN/m²
- Design value of exceptional snow load on the ground : sad = 1.0 kN/m²
C2 – Wind
NF EN 1991-1-4/NA (march 2008) + A1 (july 2011) + A2 (september 2012) + A3 (april 2019)
- Zone : 2(vb,0 = 24.0 m/s)
- Criteria for zoning : THEOULE-SUR-MER, ALPES-MARITIMES (06)
- Zone cdir : 3
| Sectors | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sector definition | from 330 ° to 60 ° | from 60 ° to 150 ° | from 150 ° to 240 ° | from 240 ° to 330 ° |
| Fundamental value of the basic wind velocity vb,0 | 24.0m/s | |||
| Shape parameter K | 0.2 | |||
| Exponent n | 0.5 | |||
| Annual probability of exceedence p | 0.02 | |||
| Probability factor cprob | 1.0 | |||
| Directional factor cdir | 1.0 | 0.85 | 0.85 | 1.0 |
| Basic wind velocity vb | 24.0m/s | 20.4m/s | 20.4m/s | 24.0m/s |
| Reference roughness length z0,II | 0.05m | |||
| Roughness length z0 | 0.5m | 0.005m | 0.005m | 0.5m |
| Terrain factor kr | 0.223 | 0.162 | 0.162 | 0.223 |
| Height above ground z | 8.0m | |||
| Minimum height zmin | 9.0m | 1.0m | 1.0m | 9.0m |
| Roughness factor cr(z) | 0.645 | 1.193 | 1.193 | 0.645 |
| Obstacle type | isolated hills | |||
| Exposure type | – | upwind | – | downwind |
| Factor depending on the type and dimensions of the obstacle s max | 0.0 | 0.8 | 0.0 | 0.8 |
| Orography factor * co(z) | 1.0 | 1.235 | 1.0 | 1.112 |
| Mean wind velocity vm(z) | 15.5m/s | 30.1m/s | 24.3m/s | 17.2m/s |
| Turbulence factor kl | 0.923 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.923 |
| Standard deviation of the turbulence σv | 4.943m/s | 3.299m/s | 3.299m/s | 4.943m/s |
| Turbulence intensity Iv(z) | 0.319 | 0.11 | 0.136 | 0.287 |
| Air density ρ | 1.225kg/m3 | |||
| Exposure factor ce(z) | 1.347 | 3.84 | 2.774 | 1.55 |
| Peak velocity pressure qp(z) | 475.1N/m2 | 978.9N/m2 | 707.1N/m2 | 546.7N/m2 |
| Peak wind velocity for Serviceability Limit States vp(z),SLS | 100.3km/h | 143.9km/h | 122.3km/h | 107.6km/h |
| Peak wind velocity for Ultimate Limit States vp(z),ULS | 122.8km/h | 176.3km/h | 149.8km/h | 131.7km/h |
C3 – Seism
Code of the Environment – Article D563-8-1 (09/01/2015)
JORF n°0248 du 24/10/2010 texte N°5
- Zone : 2(0,7 m/s²)
- Criteria for zoning : THEOULE-SUR-MER, ALPES-MARITIMES (06)
- A seismic analysis may be required for this building. You can check if your building is concerned on LEGIFRANCE