
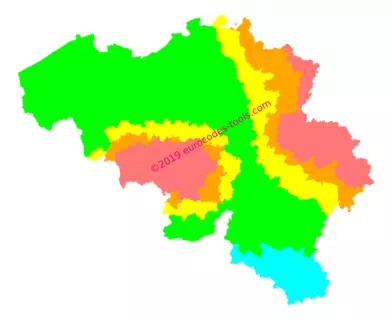
What are the Belgian seismic zones according to Eurocode 8 (NBN EN 1998-1 ANB) ?
In Belgium, the division is specified in the national annex to Eurocode 8 (The map below was created from this data). The Belgian area is divided into five seismic zones identified from 0 to 4.
| Zone | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sismicité agr | – | 0.39 m/s2 | 0.59 m/s2 | 0.78 m/s2 | 0.98 m/s2 |
Is my new building concerned ?
In Belgian regulations, the zones considered to be zones with very low seismicity are the zones for which the product agS( with ag = γI. agr does not exceed 0.06g (0.59m/s²). Here’s a summary to find out if your building is affected:
| Zone/Ground type | A | B | C | D | E |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zone 0 | No | ||||
| Zone 1 | No | Yes (except I and II) | Yes (except I) | ||
| Zone 2 | Yes (except I and II) | Yes | |||
| Zone 3 | Yes | ||||
| Zone 4 | Yes | ||||
The soil factor S is depending of the stratigraphic profile of the ground and the type of recommended elastic response spectra with respect to the surface-wave magnitude.
| Ground type | Description of stratigraphic profile | S parameter for spectrum type 2 |
|---|---|---|
| A | Rock or other rock-like geological formation, including at most 5m of weaker material at the surface. | 1,0 |
| B | Deposits of very dense sand, gravel, or very stiff clay, at least several tens of metres in thickness, characterised by a gradual increase of mechanical properties with depth. | 1,35 |
| C | Deep deposits of dense or medium-dense sand, gravel or stiff clay with thickness from several tens to many hundreds of metres. | 1,5 |
| D | Deposits of loose-to-medium cohesionless soil (with or without some soft cohesive layers), or of predominantly soft-to-firm cohesive soil. | 1,8 |
| E | A soil profile consisting of a surface alluvium layer with Vs values of type C or D and thickness varying between about 5m and 20m, underlain by stiffer material with Vs>800m/s. | 1,6 |
Buildings are classified in 4 importance classes, depending on the consequences of collapse for human life, on their importance for public safety and civil protection in the immediate post-earthquake period, and on the social and economic consequences of collapse.
Each importance class is attached to an importance factor γI
| Importance class | Buildings | γ I |
|---|---|---|
| I | Buildings of minor importance for public safety, e.g. agricultural buildings, etc. | 0.8 |
| II | Ordinary buildings, not belonging in the other categories. | 1.0 |
| III | Buildings whose seismic resistance is of importance in view of the consequences associated with a collapse, e.g. schools, assembly halls, cultural institutions etc. | 1.2 |
| IV | Buildings whose integrity during earthquakes is of vital importance for civil protection, e.g. hospitals, fire stations, power plants, etc. | 1.4 |
Eurocodes Zoning allows you to obtain seismic zones in Belgium free of charge from a GPS point.
B1 – Localization
- Coordinates in World Geodetic System 1984 (WGS84) 4.9053°, 50.2445°
- Coordinates in Belgian Geodetic System 2008 (Lambert 2008) 688279m, 603864m
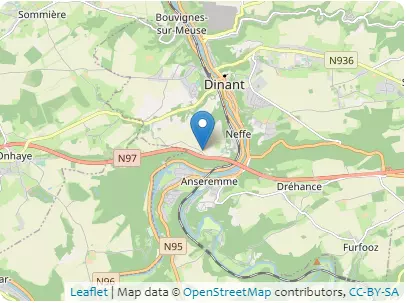
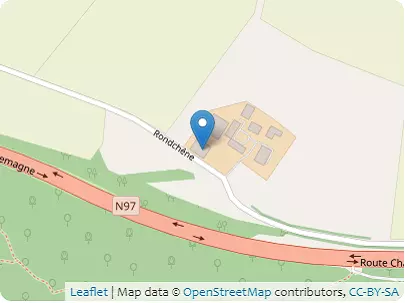
Address Rondchêne, 5500 Dinant, Wallonie
B2 – Altitudes
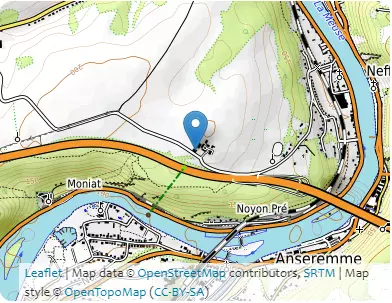
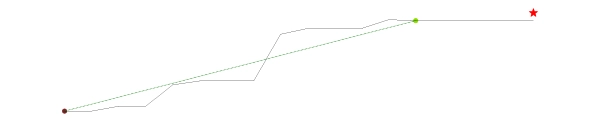
| Coordinates | 4.9013°, 50.241° | 4.9044°, 50.2436° | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elevations | 96m | 189m | ||
| Obstacle effective height H | 93m | |||
| Slope actual length Lu / Ld | 361.4m | |||
| Slope angle Φ | 25.7% | |||
| Horizontal distance site/top x | 121.2m | |||
| Elevation at the place of construction | 197m | |||
B3 – Building
- Type of building : common building with floors (apartments and/or office spaces)
- Design working life category : 100 years
- Max height : 7.0m
- Orientation from North : 35°
B4 – Terrain categories
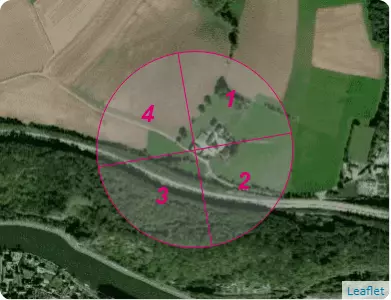
| Sectors | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Categories | II | II | III | II |
C1 – Snow
NBN EN 1991-1-3 ANB (october 2007)
- Zone Belgium : (sk,0 = 0.5 kN/m²)
- Criteria for zoning : Dinant, Namur
- Characteristic value of snow on the ground at the relevant site : sk,197 = 0.613 kN/m²
- Ground snow load with a return period of 100 years : s100 ans = 0.695 kN/m²
C2 – Wind
NBN EN 1991-1-4 ANB (december 2010)
- Zone : 24.0 m/s
- Criteria for zoning : Dinant, Namur
- Zone cdir : Belgium
| Sectors | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sector definition | from 350 ° to 80 ° | from 80 ° to 170 ° | from 170 ° to 260 ° | from 260 ° to 350 ° |
| Fundamental value of the basic wind velocity vb,0 | 24.0m/s | |||
| Shape parameter K | 0.2 | |||
| Exponent n | 0.5 | |||
| Annual probability of exceedence p | 0.01 | |||
| Probability factor cprob | 1.038 | |||
| Directional factor cdir | 1.0 | 0.983 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Basic wind velocity vb | 24.9m/s | 24.5m/s | 24.9m/s | 24.9m/s |
| Reference roughness length z0,II | 0.05m | |||
| Roughness length z0 | 0.05m | 0.05m | 0.3m | 0.05m |
| Terrain factor kr | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.215 | 0.19 |
| Height above ground z | 7.0m | |||
| Minimum height zmin | 2.0m | 2.0m | 5.0m | 2.0m |
| Roughness factor cr(z) | 0.939 | 0.939 | 0.678 | 0.939 |
| Obstacle type | cliffs | |||
| Exposure type | – | – | downwind | – |
| Factor depending on the type and dimensions of the obstacle s max | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.598 | 0.0 |
| Orography factor * co(z) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.308 | 1.0 |
| Mean wind velocity vm(z) | 23.4m/s | 23.0m/s | 22.1m/s | 23.4m/s |
| Turbulence factor kl | 0.995 | 0.995 | 1.247 | 0.995 |
| Standard deviation of the turbulence σv | 4.713m/s | 4.634m/s | 6.696m/s | 4.713m/s |
| Turbulence intensity Iv(z) | 0.201 | 0.201 | 0.303 | 0.201 |
| Air density ρ | 1.225kg/m3 | |||
| Exposure factor ce(z) | 2.124 | 2.124 | 2.456 | 1.124 |
| Peak velocity pressure qp(z) | 824.7N/m2 | 797.5N/m2 | 953.3N/m2 | 824.7N/m2 |
| Peak wind velocity for Serviceability Limit States vp(z),SLS | 130.8km/h | 128.6km/h | 140.6km/h | 130.8km/h |
| Peak wind velocity for Ultimate Limit States vp(z),ULS | 160.2km/h | 157.5km/h | 172.2km/h | 160.2km/h |
C3 – Seism
NBN EN 1998-1 ANB (october 2011)
- Zone : 1 (0,39 m/s²)
- Criteria for zoning : Dinant, Namur
- A seismic analysis may be required for this building.